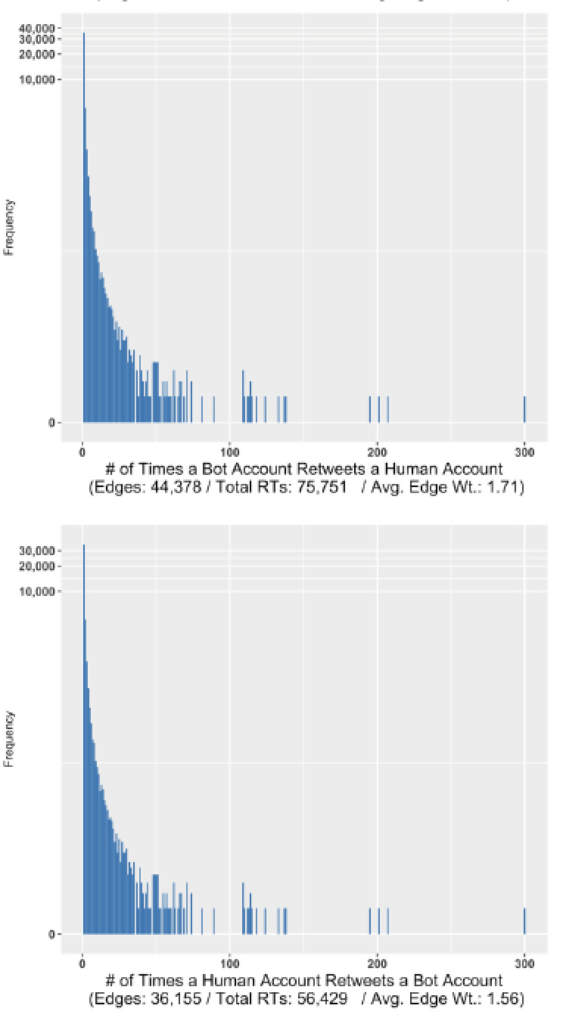
The emergence of social bots within online social networks (OSNs) to diffuse information at scale has given rise to many efforts to detect them. While methodologies employed to detect the evolving sophistication of bots continue to improve, much work can be done to characterize the impact of bots on communication networks. In this study, we present a framework to describe the pervasiveness and relative importance of participants recognized as bots in various OSN conversations. Specifically, we harvested over 30 million tweets from three major global events in 2016 (the U.S. Presidential Election, the Ukrainian Conflict and Turkish Political Censorship) and compared the conversational patterns of bots and humans within each event. We further examined the social network structure of each conversation to determine if bots exhibited any particular network influence, while also determining bot participation in key emergent network communities. The results showed that although participants recognized as social bots comprised only 0.28% of all OSN users in this study, they accounted for a significantly large portion of prominent centrality rankings across the three conversations. This includes the identification of individual bots as top-10 influencer nodes out of a total corpus consisting of more than 2.8 million nodes.
